
You also need to steer the beam at near-black.
#Do older cathode ray tubes emit blue light how to
How to accurately steer the beam ? Magnetic deflection is relatively slow.Where to get the indexing information from ? A current sensor in the anode at 30 kV ? A light sensor, using invisible light ?.An electron beam fundamentally cannot be narrow at high current, due to electron repulsion.Opportunities for flat faceflate and/or shallow cone.Thinner gun (only 1 cathode), thinner neck, lower volume of magnetic field, more efficient deflection.
Repeat 3 times for 3 colors.ģ times higher efficiency due to absence of shadow mask. Using position feedback information, a narrow electron beam can be made to scan over 1 phosphor stripe. Writing 3 colors with 1 beam has been tried, this is called a "beam-index tube". Of course modern non CRT TVs do not work this way and are actually pixel driven. In fact it is quite remarkable that they managed to make CRTs as good as they did.
#Do older cathode ray tubes emit blue light tv
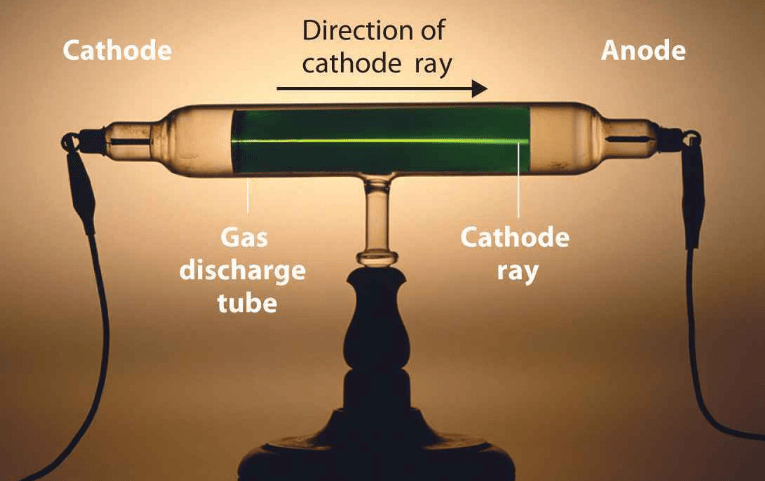
You have to remember at the time colour TV was invented vacuum tubes were still the norm and transistorized TV's were still a pipe-dream. With no feedback of where the beam is actually hitting the phosphor you are extremely sensitive to temperature changes in the tube and the electronics and mechanical variations. In fact the TV has no idea how many pixels are on the screen.Ĭould that be done today with a single gun and high frequency control over a single very tightly focussed electron beam, possibly, but it would not be a simple matter. The beam is larger than the holes in the screen. That is, the red gun can only shine on red phosphor, green on green, and blue on blue. The screen effectively creates a shadow everywhere except where the appropriate coloured phosphor is. The beams then must pass through a screen of holes. In order to do that the inventors of colour television came up with a clever trick of having three guns fire at the screen at a slight angle. Unfortunately in order to keep the colours crisp you do not want the red information painting over the green and blue, and vica-versa. This information is separated to generate the red, green, and blue intensity levels for the beam as it tracks across. A colour TV needs to paint three colours on the screen.Ī classical TV signal has the three color channels mixed into a single signal and time multiplexed. This inward facing stripe produced bursts of light that were caught by a photomultiplier built into the CRT, and these pulses were used to keep the color multiplexing circuit in sync with the actual beam position.Ī monochrome TV has only one gun that paints lines across the screen. It used vertical stripes of phosphor, with an extra inward-facing stripe included in each group. That said, there was at least one experimental design that did use a single gun and time-division multiplexing of the colors. If you had a single electron gun and no shadow mask, the phosphor dots would have to be somewhat larger than the beam diameter in order to prevent "bleeding" among the colors, which would make them objectionably large ("grainy") when viewed. Remember, the phosphor dots are MUCH smaller than the diameter of the electron beam when it reaches the screen.

It is the distinct angle of arrival that makes sure that each electron beam excites only the color that it is supposed to. It would have been extremely difficult to sequence three colors through a single electron gun with the technology available at the time.Īlso, the separate guns allow the separate excitation of the corresponding sets of phosphor dots through the shadow mask precisely BECAUSE they are in physically distinct locations. The first color TVs were built entirely from analog components.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
